In today’s world, technology dominates everything from the simplest to the most complex of activities. Software is undoubtedly the primary need of the market. Most organizations are trending towards cloud and multi-cloud implementations.
This move is not surprising since many are shifting to working remotely, and cloud computing has its share of benefits and challenges.
What is SaaS?
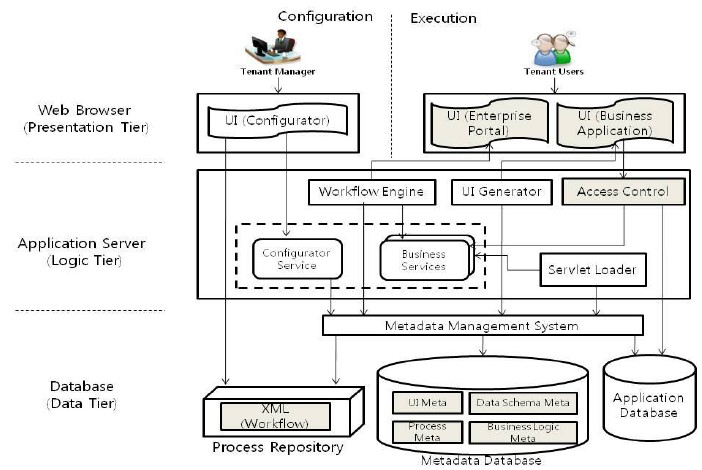
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) is typically an on-demand, cloud-based software delivery service model. Besides, it is also a cloud-based way of delivering software and apps. If you choose to subscribe to this model, you can access apps without hosting them in-house; users don’t install or run the software on their devices.
As long as you have an internet-connected device, you can access the SaaS framework no matter where you are. This is especially useful for teams working remotely across the globe. Therefore, the managers looking to increase the productivity of their remote teams.
Organizations don’t need to build infrastructure and maintain it to provide the necessary apps to the staff. In brief, SaaS helps businesses grow faster in a tech-friendly world.
Benefits of SaaS
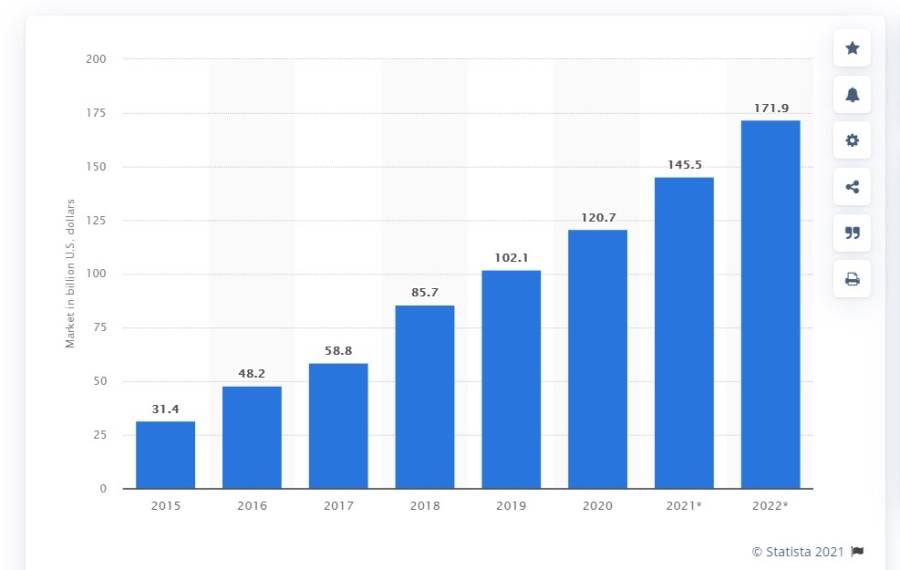
The future of the global SaaS is bright, and its adoption is expected to grow. This encouraging growth is due to:
- Scalable resources – Organizations can upscale or downscale resources on-demand, as and when needed.
- Pay only what you use – Since organizations purchase on an as-needed basis, they only pay for what they use.
- Quick and easy adoption – There’s no waiting period. Organizations can gain access instantly and provision employees. This is unlike on-site applications that need more time to deploy.
- Monthly or yearly subscription fees – These are relatively cheaper, making it an economical choice for growing businesses.
- Updates and maintenance – These are all handled by the SaaS provider, relieving the organization to focus on other pressing matters.
- No infrastructure or staff costs – You’re going in remotely; you can access the SaaS platform from a web browser 24/7. You don’t need to pay for any in-house hardware and software licenses; Also, no need to hire much on-site staff to maintain and support either the infrastructure or software.
- Application Programming Interface (API) integration – SaaS can easily integrate with other software via standard APIs.
- Security – SaaS providers invest heavily in security, for instance by distributing servers across multiple geographical locations with automated backups.
Understanding the need for SaaS security
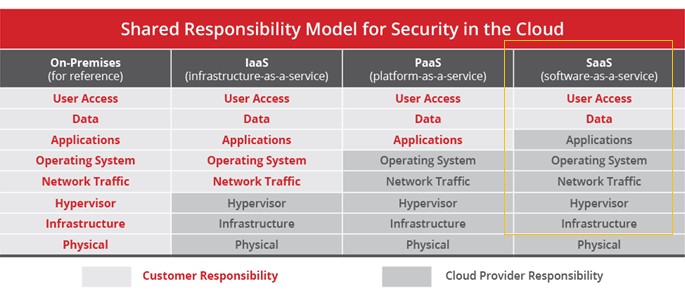
Many SaaS providers host and provide SaaS services, security, and maintenance to their users. SaaS security is typically cloud-based security designed to protect all software and data that the service carries. It’s a set of best practices that organizations that store data in the cloud put in place to secure their information. The SaaS provider is expected to secure the platform, network, apps, operating system, and whole infrastructure.
Although SaaS security is the provider’s sole responsibility, both the customer and the service provider share equal responsibilities. Both are required to adhere to SaaS security guidelines by the National Cyber Security Center (NCSC) in the UK, for example.
Cybercriminals tend to target SaaS environments because they have a large amount of confidential data. Data safety and integrity will compromise in the event of a security breach. Data safety and integrity will compromise in the event of a security breach. This can translate into massive financial loss. You don’t need us to remind you of the consequences. Any hacker successfully gains access to a SaaS environment; spells disaster of the highest degree.
So, if vendors are not delivering up to par services at all times, you might end up experiencing service disruptions or security breaches often. Therefore, before you sign up for any SaaS service, read the Service Level Agreement (SLA) thoroughly and throw the questions to the provider.
Businesses must ensure that they are carrying out the best practices. If not, businesses will fail, not to mention the many legal implications that will follow suit. Simply put, organizations that utilize the SaaS model must prioritize SaaS security. It involves not just the practical aspect of securing the environment but ensuring proper certifications are in place.
SaaS security challenges
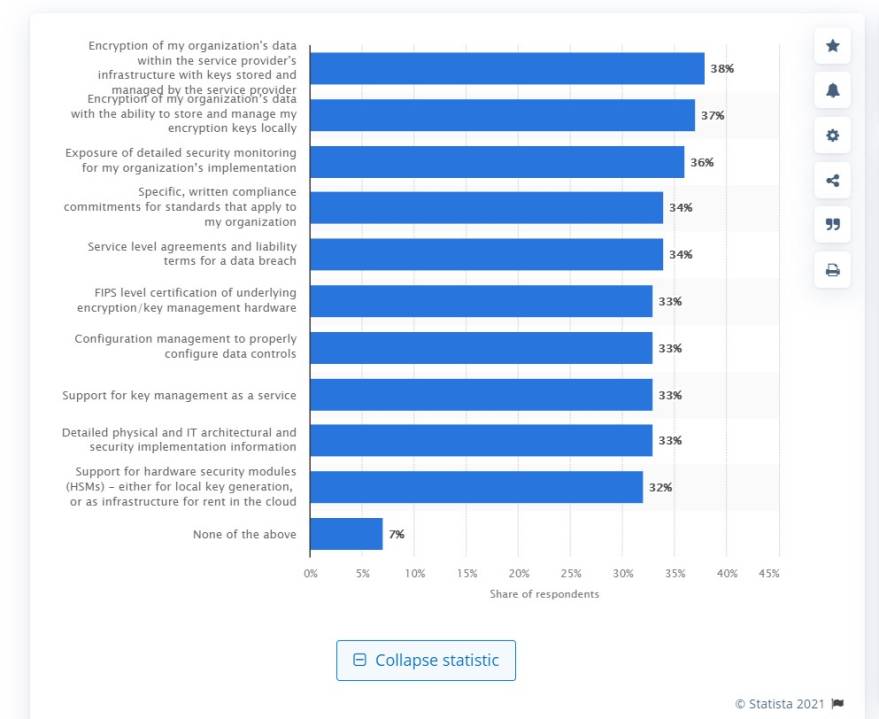
There is a range of challenges that SaaS brings to the table:
Complexity
As explained, SaaS resides in the cloud and caters to various teams across an organization and sometimes across the globe. SaaS applications are heavily used across the board by tons of users. All users are at different levels, holding different roles, not to mention varying levels of technical knowledge.
It makes SaaS applications tricky even for specialist security teams to grasp.
Communication
This is a common problem that occurs in an organization, be it when it comes to SaaS or onsite applications. The organization is hard to move forward because of the limited interaction between teams. Breakdowns in communication can also often be the root cause of security issues.
Collaboration
Often, teams have their own goals and functions, respectively. Unfortunately, most emphasize functionality and business requirements, rather than security. But, there is a real need to balance both business and security needs on an ongoing basis. This is a huge challenge that requires regularly educating your teams.
Less control
Businesses that opt for SaaS have to rely on third-party vendors to deliver secured services. Even though providers throw in everything to ensure top-notch security and operation, in reality, there will be times when there’ll be service disruption. Businesses don’t have complete control and rely on the providers for continuous uptime.
Performance issues
You usually don’t experience performance issues with cloud services. When a server shuts down, another will kick in and ensure the service will not be disrupted. Yet, you may experience some performance issues if located far from data centers. Therefore, check with your provider on their data center locations before signing up.
SaaS best practices
It is a good move to migrate your systems and processes to SaaS. But first, you need to take into consideration both your organization’s existing requirements and SaaS-specific security requirements as well.
Here are some cloud security best practices that you can upkeep to help the situation:
1. Access management and control
When offering cloud-based applications to users, your users require a means to log in to access the software. Only people with the proper permissions can access to suitable applications on the cloud. You can use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to protect the user’s privacy and secure the communication channel.
Besides, you can consider using extra security features like multi-factor authentication (MFA) or other more robust authentication methods.
The system needs to take into consideration any data requirements and workflow assignments as well.
2. Data Protection
Users communicate with SaaS applications via tons of established channels. These channels must be secured using encryption and other security tools, keeping all data safe from prying eyes. Transport Layer Security (TLS) is a widely adopted security protocol to encrypt and protect data in transit.
Also, data at rest in your servers and databases must be encrypted to ensure that it’s safe from hackers. Only by ensuring data security via adequate security measures, especially for sensitive data, can they be deployed for use. Interestingly, you can also consider SaaS-based security solutions for your cloud infrastructure.
A SaaS provider should provide client and server-side encryption with security management. It needs to complete full audit trails, especially if any hardware is deployed on-premises.
It’s good practice for you, as the customer, to control the encryption keys. Protect ALL data by encrypting in transit and at rest, to prevent a data breach. Remember that ransomware is common today and backup lifecycles may not be enough protection.
You can also design data access policies that Data Loss Prevention (DLP) enforces. This, along with technology, effectively safeguards data in cloud applications, as well as at endpoints.
3. Use antivirus/anti-malware
Deploy the necessary advanced antivirus/anti-malware programs to protect from phishing and any cyberattacks. Such programs have behavioral analytics and real-time threat intelligence to help detect and block attacks and malicious files from spreading through cloud email and file-sharing applications.
4. CASB tools
Cloud Access Security Broker, aka CASB, is cloud-hosted software or on-site software/ hardware that functions as the intermediary between users and SaaS providers. It’s used to give you much-needed visibility. It enables you to extend the reach of your organization’s security policies from the on-site infrastructure to the cloud. You’re also allowed to design new policies specific to cloud use, too.
CASB typically serves as a policy enforcement center. It combines various types of security policies in the cloud so that businesses can safely use the cloud. Also, take some time to look into any shortcomings in the SaaS provider’s security features, as you can use CASB tools to help address these.
CASB tools can help remove any security misconfigurations and correct high-risk user activity applications. Furthermore, they can also detect any unauthorized usage of cloud services, track users’ access, and control cloud services based on user, device, and application.
Pay attention to the various CASB deployment modes and choose the best one that fits your organization.
5. Monitoring
Like any other technology security, frequent updates are crucial. As such, SaaS providers must update their standardized Virtual Machine (VM) images and software. You must monitor and track all SaaS usage. Likely, information can prove helpful to detect any abnormalities or unexpected behavior.
Examine the data collated from tools like CASBs. Analyze the logs provided by the SaaS provider. Be proactive, especially when it comes to security. Use a combination of automation and manual tools within the SaaS management systems, along with systematic risk management. So that you can keep in touch with any evolving SaaS usage, unexpected behavior, or anything suspicious.
These measures are essential to ensure that users use SaaS safely while you always stay ahead and on top of things.
6. Network control
It is important to have security group control configured to access specific instances across the network. This can include jump servers and Network Access Control Lists (NACL). Controlling at the network level provides an additional layer of security for virtual private clouds. This acts as a firewall to control and track traffic to and from the subnets.
Such control at the network layer helps filter dangerous or suspicious traffic. This is done based on a pre-configured set of rules about the permitted types of traffic on the network. On top of that, some even implement higher protection such as prevention systems (IDS/IPS); these watch for suspicious traffic even after the firewall.
7. Proper governance and incident management
This means putting in place the necessary Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for all types of incidents. Likewise, they have to capture, note, report and track to closure. The SOPs should cover the investigation procedures even for any potential security breaches.
8. Scalability and reliability
Many go for SaaS because of its capability to do vertical and horizontal scaling. The size of the server restricts the former while the latter focuses on the means to connect multiple hardware or software entities so that they can still function as a single unit. To cater for this, a SaaS provider must have sufficient redundancy in the infrastructure to ensure continuity of service.
This is a best practice that all SaaS providers should have in place. Last but not least, there should be a reliable Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) in place to mitigate any disasters.
Conclusion
Cloud computing will evolve with time and will gain even bigger momentum in the future. SaaS technology promises you a more agile performance and higher scalability at lower costs. As such, business will prefer the SaaS framework.
With the right technology deployed and best practices in place, SaaS can be a serious contender, far better and more secure than on-site applications, even for those in critical financial and regulatory areas. There are ways to overcome SaaS challenges and help your business grow with time.
Author Profile
Beh always shares her thoughts and experiences on the Internet. As a digital marketer, she loves to meet and build relationships with different people. Reach out to her on LinkedIn or WebRevenue.
Image Credit: Inner post images provided by the author; Thank you!
Top Image Credit: Tima Miroshnichenko; Pexels; Thank you!
The post What is SaaS Security? Benefits, Challenges, and Best Practices appeared first on ReadWrite.


Comentarios recientes